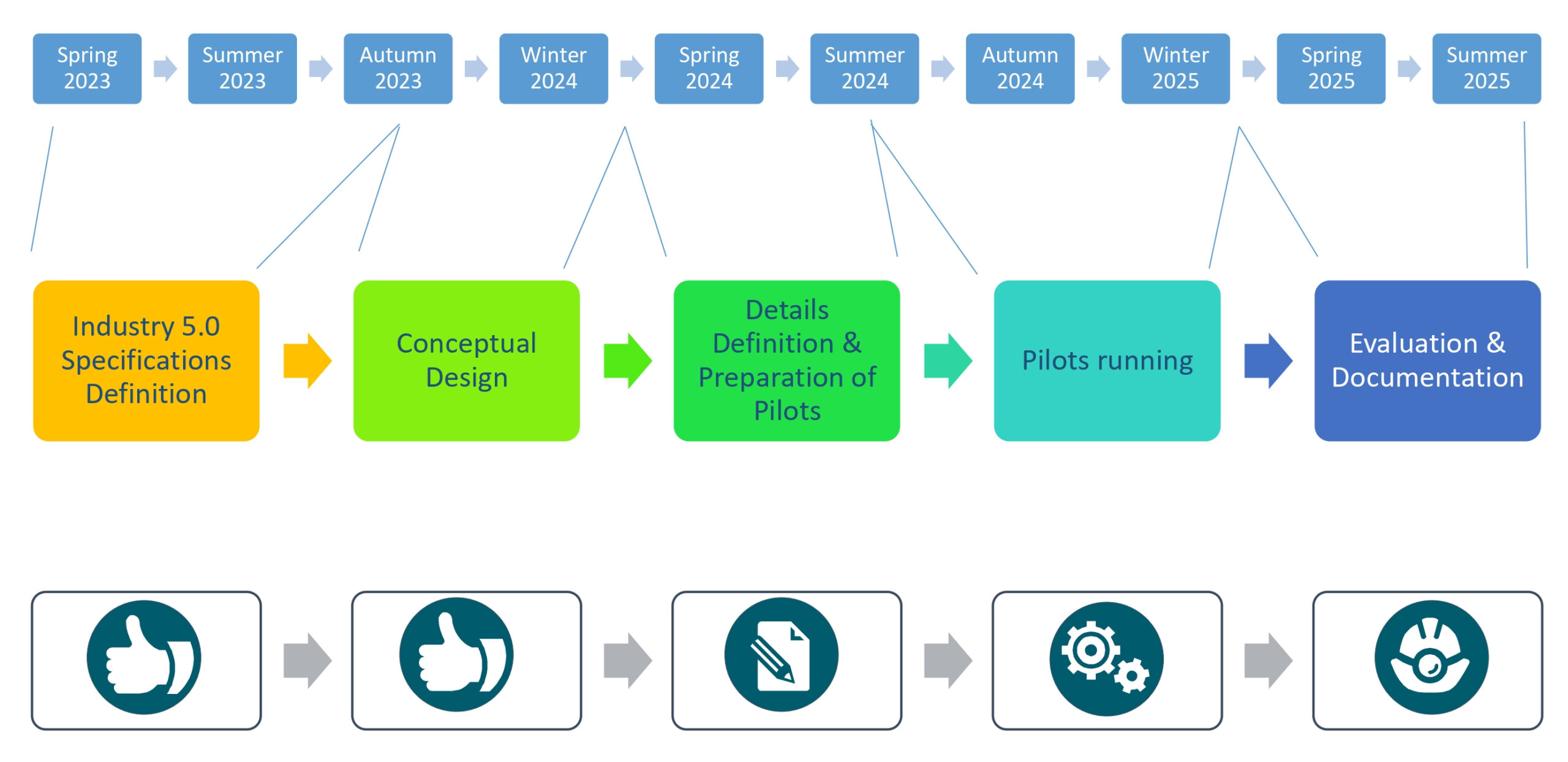
BRIDGES 5.0 is dedicated to evaluating and enhancing two established forms of training intervention, namely Teaching and Learning Factories. These interventions are designed to address the skills required in manufacturing industry, targeting both individual companies and associations of public-private organisations. The objective of these interventions is to facilitate skill adaptation in response to the Industry 5.0 paradigm shift.
Within this framework, the focus is on job transitions, the digitisation of work, and three critical aspects: human-centric job roles, environmental sustainability, and production resilience. Social factors are also considered. We aim to transform the concepts of Teaching and Learning Factories into a procedure that promotes experiential learning, specifically tailored to identify skills for Industry 5.0, rooted in problem-solving the manufacturing environment.
Teaching Factories.

| Name of organisation | Comau S.p.A. |
| Country | Italy |
| Sector | Robotics & Automation in manufacturing |
| Main activity | Automation and robotics |
| Focus of intervention | An outdoor automation solution to improve quality, performance and well-being during labor-intensive welding operations |
Summary of the problem and the intervention
The focus is on agility of welders; enhancing this requires a mobile robotic welding solution in collaboration with operators. The aim of the intervention is to prepare a workforce that can use enhanced processes to improve quality, performance and well-being during labour-intensive welding tasks.

| Name of organisation | Infineon Technologies Austria AG |
| Country | Austria |
| Sector | Semiconductors |
| Main activity | Semiconductors manufacturing |
| Focus of intervention | Changing the operational setup with centralized remote control and multiple data-based decision-making |
Summary of the problem and the intervention
The problem is that the workforce is not used to work with system provided decision proposals, from multiple sources, in a centralized manner. The intervention focuses on employees empowerment to facilitate the work performed within the new organizational and operational structure. It also focuses on technologies that support the decision-making process, as the goal is for employees to receive data from different areas and make the best decision.



| Name of organisation | Matz-Erreka S. Coop. Eika S. Coop. Mondragon S. Coop. |
| Country | Spain |
| Sector | Manufacturing |
| Main activity | A wide range of parts for applications in different sectors such as automotive or bio-health/domestic appliances for the cooking sector |
| Focus of intervention | Workplace improvement to foster attitudinal and behavioural changes |
Summary of the problem and the intervention
The problem for both companies is how to design the workplace so that people are empowered and benefit from the automation process. The intervention aims to address any employee skills shortages that limit the adoption of new technology. This means that they are trained in automation in such a way that they can easily incorporate this knowledge into their professional daily life.


| Name of organisation | Kitron UAB Hybrid Labs UAB |
| Country | Lithuania |
| Sector | Batteries |
| Main activity | Electronics manufacturing Services |
| Focus of intervention | Empowerment of employees about decision-making and working with digital technologies |
Summary of the problem and the intervention
The problem is to keep employees motivated in their work subject by expanding the educational process with different scenarios and changing the work roles in them. The intervention aims to provide skills to workers and make them want to be at the center of managing and operating machinery with wider decision-making authority.